
A
weekly e-journal by Art Epstein, OD, FAAO
Off the Cuff: Dry Eye and the Contact Lens Rabbit Hole
Online contact lens sellers think that they can make a killing selling antiquated lens materials to millennials, who often place convenience ahead of common sense, but that’s not going to be as easy as they think. Digital device overuse, poor diet and a host of other factors of modern life are fueling an epidemic of “dry eye.” Those same factors are also making it more and more difficult to keep contact lens wearers comfortable.
|
|||||
 |
||
| Recurrent Corneal Erosions in Epithelial Corneal Dystrophies | ||||
Authors wrote that the corneal epithelium is the most important structure of the ocular optical system and that recurrent corneal erosions can result from inflammation, trauma, degeneration and dystrophies. Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD), epithelial recurrent erosion dystrophy (ERED), and Francheschetti and Meesmann's epithelial corneal dystrophy (MECD) can all—in addition to other signs and symptoms—result in more or less frequent corneal erosions though the pathomechanisms involved are different, they added. The authors wrote further that in EBMD, corneal erosions are facultative and clinical signs are often subtle. Furthermore, aberrant basement membrane structures are associated with thinning of the epithelium and can be clinically identified as maps or fingerprints. In ERED, recurrent corneal erosions are predominantly in the first decades of life, but always present, and a defect in the COL17A1 gene results in a dysfunctional hemidesmosome, the authors reported. In MECD, punctate corneal erosions are less frequent and result from intraepithelial microcysts, which open spontaneously onto the ocular surface, the authors also noted. Usually lubricants, therapeutic contact lenses, and sometimes epithelial debridement and phototherapeutic keratectomy are the mainstay for treating corneal erosions in these three dystrophies, authors wrote. |
||||
SOURCE: Geerling G, Lisch W, Finis D. Recurrent corneal erosions in epithelial corneal dystrophies. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2018;235(6):697-701. |
||||
 |
||
| Agreement Between Internal and Posterior Corneal Astigmatism in Pseudophakic Eyes | ||||
This prospective study enrolled 32 eyes of 32 patients (18 women, 56.3%) who underwent phacoemulsification with implantation of a non-toric monofocal intraocular lens (IOL) to directly measure internal astigmatism and evaluate its agreement with posterior corneal astigmatism in pseudophakic eyes. Two months postoperatively, posterior corneal astigmatism was measured using a Pentacam Scheimpflug analyzer (Oculus). Manifest refractive astigmatism was measured after fitting a spherical hard contact lens. This refractive astigmatism, which was vertexed to the corneal plane, was considered internal astigmatism. The magnitudes of internal and posterior corneal astigmatism were compared. And the relationship and agreement between the two astigmatisms were investigated using the Spearman correlation coefficient and Bland-Altman plots, respectively.
The mean patient age was 56.3 ± 9.6 years. IOL decentration or tilt and posterior segment abnormalities were not encountered in any cases postoperatively. The mean refractive astigmatism measured before fitting the hard contact lens was -0.81D ± 0.56D. Internal astigmatism (-0.17D ± 0.21D) was significantly different from posterior corneal astigmatism (-0.30D ± 0.15D). Regression analysis demonstrated a weak association between internal astigmatism and posterior corneal astigmatism (r2 = 0.22). Bland-Altman plots produced 95% limits of agreement for these two astigmatisms from -0.49D to 0.75D. A significant but weak correlation was found between the magnitudes of internal astigmatism and posterior corneal astigmatism in the pseudophakic eyes. This result indicates that Pentacam measurement of the posterior cornea did not compare well with a "gold standard" of refraction-derived values. |
||||
SOURCE: Feizi S, Delfazayebaher S, Javadi MA. Agreement between internal astigmatism and posterior corneal astigmatism in pseudophakic eyes. J Refract Surg. 2018;34(6):379-86. |
||||
 |
||
| Simplified Method for Rapid Field Assessment of Visual Acuity by First Responders After Ocular Injury | ||||
Researchers wrote that initial visual acuity after ocular injury is an important measure, as it is an accurate predictor of final visual outcome and gives a rapid estimation of the overall severity of the injury, thereby aiding evacuation prioritization. So they devised a simple method for rapidly assessing visual acuity in the field without having to rely on formal screening cards. Using common objects, icons and information found in the injury zone—for example, common military name tapes, rank insignias, patches, emblems and helmet camouflage bands (i.e., Army Combat Optotypes [ACOs])—researchers devised a Snellen-equivalent method of assessing visual acuity, and correlated the measurement to the ocular trauma score (OTS).
The ability to read the ACOs at two, three and five feet correlated with acuities in the range from 20/20 to 20/400. Identification of ACOs with visual acuity of 20/50 and 20/200 approximated important inflection points of severity for the OTS. Researchers concluded that accurately assessing visual acuity in the field after ocular injury provided essential information, but did not require sophisticated screening equipment. They added that pertinent and accurate acuities could be rapidly estimated using commonly available text or graphical icons such as standard name tapes, patches and rank insignias. |
||||
SOURCE: Godbole, NJ, Seefeldt, ES, Raymond, WR, et al. Simplified method for rapid field assessment of visual acuity by first responders after ocular injury. Military Medicine. 2018; 183, 3/4:219. |
||||
|
|||
| News & Notes | ||||||||
Allergan Announces Positive Topline Phase III Data for Bimatoprost SR Implant
|
||||||||
| SynergEyes & Brien Holden Vision Institute Join Forces for Specialty Contact Lens Development SynergEyes is partnering with the Brien Holden Vision Institute to deliver advanced, customized vision correction for myopes and presbyopes. The exclusive worldwide licensing agreement will enable the manufacturing of design technologies developed by the Brien Holden Vision Institute and augmenting the SynergEyes presbyopic package by offering the latest designs on the hybrid contact lens platform. The tailored hybrid contact lens will be designed to meet the needs of myopes and presbyopes, and deliver precise correction and a high degree of comfort. Read more. |
||||||||
| Bausch + Lomb Introduces Ocuvite Blue Light Eye Vitamins & Soothe Xtra Protection Preservative-free Lubricant Eye Drops Bausch + Lomb introduced Ocuvite Blue Light eye vitamins, a nutritional supplement formulated with lutein and zeaxanthin, two carotenoid pigments naturally found in the eye. This formulation includes high levels of lutein designed to help protect eyes from the blue light that reaches the macula. The vitamins contain 25mg of lutein and 5mg of zeaxanthin isomers, key eye nutrients that help absorb blue light before it reaches the macula. They will be available for purchase at major retailers in the third quarter of 2018. Read more. In addition, the company introduced Soothe Xtra Protection (XP) Preservative Free lubricant eye drops, expanding its portfolio of eye health products to meet the growing demand for dry eye symptom relief without the use of preservatives. The eye drops, which use a unique combination of Restoryl mineral oils as active ingredients to restore the lipid layer, seal in moisture and protect against further irritation, will be available at many major retailers nationwide, including Walmart, Target, Walgreens, Rite Aid and Meijer by the end of June. Read more. |
||||||||
| CMS Issues Preliminary Decision on J Code for Avedro Photrexa Drug Formulations Avedro announced that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services issued a preliminary decision to establish a product-specific Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System J code for Photrexa drug formulations. Claims submitted with a product-specific J code are generally processed more efficiently than claims using a miscellaneous code (J3490), which requires manual review. Photrexa formulations are the only drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in conjunction with the KXL System in corneal collagen cross-linking to treat progressive keratoconus and corneal ectasia following refractive surgery. Read more. |
||||||||
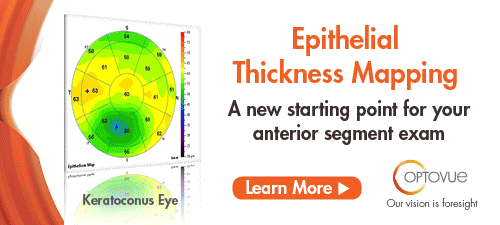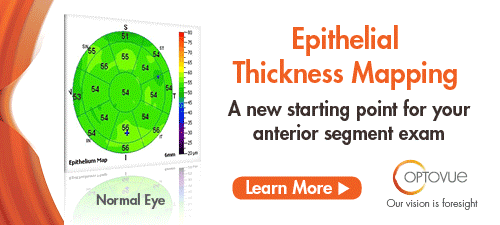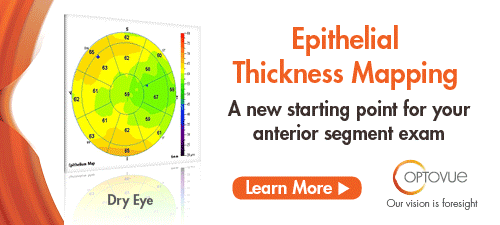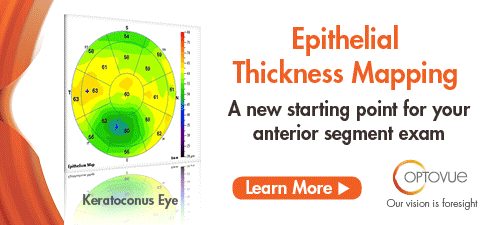
| Optovue Gets FDA Nod for Epithelial Thickness Mapping Optovue received expanded FDA 510(k) clearance for non-contact, quantitative measurements of the epithelial and stromal layers of the cornea, i.e., epithelial thickness mapping. The expanded clearance adds a 9mm ETM scan to the previously available 6mm map. Optovue’s ETM, now available on the Avanti Widefield OCT system, is the first FDA-cleared product indicated to provide corneal epithelial and stromal measurements that aid in the diagnosis, documentation and management of ocular health and diseases in the adult population. ETM was previously cleared on the company’s iVue system in 2017. Read more. |
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Optometric Physician™ (OP) newsletter is owned and published by Dr. Arthur Epstein. It is distributed by the Review Group, a Division of Jobson Medical Information LLC (JMI), 11 Campus Boulevard, Newtown Square, PA 19073. HOW TO ADVERTISE |



